The telecommunications industry continues to evolve rapidly, demanding increasingly sophisticated filtering solutions that can handle complex signal processing requirements. Modern wireless communication systems, satellite networks, and radar applications rely heavily on advanced filtering technologies to ensure optimal performance and signal integrity. Among the most critical components in these systems are specialized filtering devices that can effectively separate desired signals from unwanted interference while maintaining exceptional electrical characteristics and thermal stability.
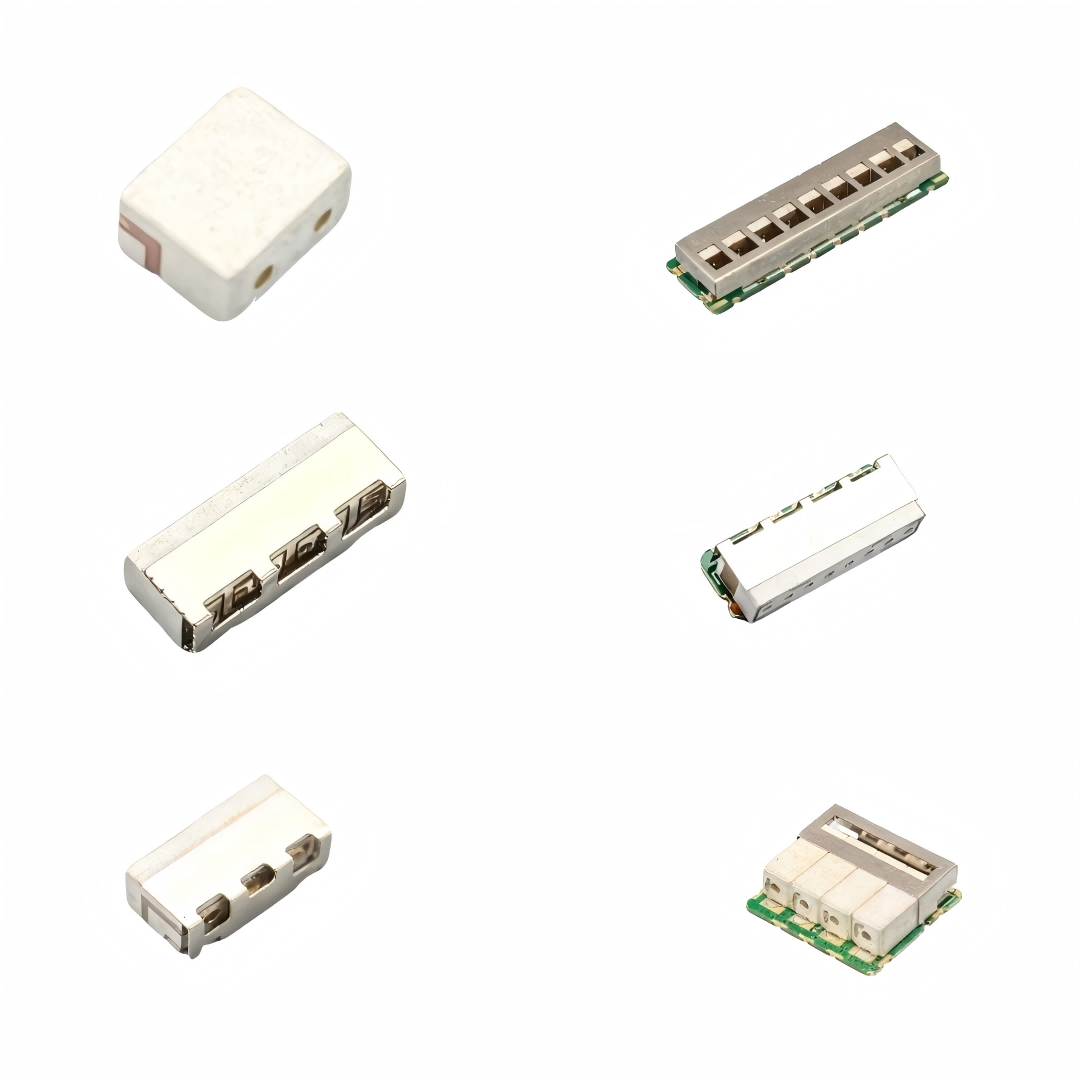

Engineering teams across various industries are increasingly turning to ceramic-based filtering solutions due to their superior performance characteristics and reliability. These advanced components offer exceptional temperature stability, low insertion loss, and high power handling capabilities that make them ideal for demanding applications. The growing complexity of modern communication systems requires filtering solutions that can operate effectively across multiple frequency bands while maintaining consistent performance under varying environmental conditions.
Understanding Ceramic Filter Technology
Material Properties and Composition
The foundation of high-performance ceramic filters lies in carefully engineered dielectric materials that exhibit specific electrical and physical properties. These materials are typically composed of complex oxide compounds that have been formulated to achieve precise dielectric constants, low loss tangents, and excellent temperature coefficients. The ceramic matrix provides mechanical stability while the dielectric properties enable effective electromagnetic field control within the filter structure.
Manufacturing processes for these ceramic materials involve sophisticated powder preparation, forming techniques, and controlled sintering procedures that ensure consistent material properties throughout the final product. Quality control measures during production include precise temperature monitoring, atmospheric control, and dimensional verification to guarantee that each component meets stringent performance specifications. The resulting ceramic substrates exhibit exceptional uniformity and reliability that translates directly into consistent filter performance.
Electromagnetic Design Principles
The electromagnetic behavior of ceramic filters is governed by fundamental principles of wave propagation and resonance within dielectric media. When electromagnetic energy enters the ceramic structure, it interacts with the dielectric material in ways that create specific resonant modes and filtering characteristics. The geometry and dimensions of the ceramic elements, combined with the material properties, determine the center frequency, bandwidth, and rejection characteristics of the filter.
Design engineers utilize sophisticated electromagnetic simulation tools to optimize the ceramic structure for specific filtering requirements. These simulations account for factors such as coupling between resonant elements, parasitic effects, and electromagnetic field distributions within the ceramic medium. The ability to precisely control these electromagnetic interactions enables the development of filters with highly customized frequency responses and exceptional performance characteristics.
Performance Characteristics and Advantages
Frequency Response and Selectivity
One of the most significant advantages of ceramic filtering technology is its ability to achieve extremely sharp frequency selectivity with minimal insertion loss in the passband. The high dielectric constant of the ceramic material enables compact resonator designs that can achieve high Q-factor performance, resulting in steep filter skirts and excellent rejection of out-of-band signals. This selectivity is particularly important in applications where multiple signals must coexist in close proximity without interference.
The frequency response characteristics of ceramic filters can be tailored through careful design of the resonator geometry and coupling mechanisms. Multiple resonator configurations allow for the implementation of various filter types, including bandpass, bandstop, lowpass, and highpass responses. Advanced design techniques enable the creation of filters with multiple passbands, notches, and complex transfer functions that meet specific system requirements.
Power Handling and Thermal Performance
Ceramic materials exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and power handling capabilities that make them suitable for high-power applications. The thermal stability of the ceramic substrate ensures that filter characteristics remain consistent across wide temperature ranges, which is essential for outdoor installations and aerospace applications. The low coefficient of thermal expansion minimizes dimensional changes that could affect filter performance under varying thermal conditions.
Power handling capabilities of ceramic filters are typically limited by thermal effects rather than material breakdown, allowing for safe operation at power levels that would damage other filter technologies. The excellent heat dissipation characteristics of ceramic materials enable effective thermal management even in compact package configurations. This thermal performance advantage makes ceramic filters particularly suitable for base station applications and high-power radar systems.
Applications and Market Requirements
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Modern telecommunications networks rely extensively on advanced filtering solutions to manage the complex spectral requirements of multiple communication standards and services. Base station equipment requires filters that can handle multiple frequency bands simultaneously while providing excellent isolation between different services. The compact size and high performance of microwave dielectric ceramic filter solutions make them ideal for these demanding applications.
The deployment of 5G networks has created new challenges for filter design, including the need for wider bandwidths, higher frequencies, and more complex filtering requirements. Ceramic filter technology has evolved to meet these challenges through advances in material science and electromagnetic design techniques. The ability to integrate multiple filter functions into compact ceramic packages enables system designers to achieve the performance required for next-generation wireless infrastructure.
Satellite Communication Systems
Satellite communication applications place extreme demands on filter performance, requiring components that can operate reliably in the harsh environment of space while maintaining precise frequency characteristics over many years of service. The radiation resistance and thermal stability of ceramic materials make them particularly well-suited for these applications. Space-qualified ceramic filters undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand launch stresses, thermal cycling, and radiation exposure.
The trend toward smaller, more capable satellites has increased the demand for compact, lightweight filtering solutions that do not compromise performance. Ceramic filter technology enables the development of highly integrated systems that can provide multiple filtering functions in minimal space and weight budgets. The reliability and longevity of ceramic components are essential for satellite applications where maintenance is not possible once deployed.
Design Considerations and Selection Criteria
Electrical Specifications
Selecting the appropriate ceramic filter for a specific application requires careful consideration of numerous electrical parameters that affect system performance. Key specifications include center frequency, bandwidth, insertion loss, return loss, rejection characteristics, and power handling capability. The interaction between these parameters must be evaluated in the context of the overall system requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Temperature stability is another critical factor that affects filter selection, particularly for applications that must operate over wide temperature ranges. The temperature coefficient of frequency determines how the filter characteristics will change with temperature variations. Advanced ceramic materials can achieve temperature coefficients approaching zero, ensuring stable performance across the operating temperature range.
Mechanical and Environmental Factors
The mechanical properties of ceramic filters are important considerations for applications that must withstand vibration, shock, and mechanical stress. The inherent strength and durability of ceramic materials provide excellent resistance to mechanical damage, but proper mounting and packaging techniques are essential to ensure long-term reliability. Environmental sealing requirements may dictate specific package configurations and materials.
Size and weight constraints often play a significant role in filter selection, particularly for portable and aerospace applications. The high dielectric constant of ceramic materials enables compact filter designs that can achieve performance comparable to much larger conventional filters. Integration options, including surface-mount packages and embedded filter elements, provide flexibility for system designers working within strict space and weight limitations.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Production Processes
The manufacturing of high-performance ceramic filters involves sophisticated production processes that must maintain precise control over material properties and dimensional tolerances. Starting materials are carefully selected and processed to ensure consistent dielectric properties and minimal variation between production lots. Forming processes, including pressing and casting techniques, must achieve the precise geometries required for optimal electromagnetic performance.
Sintering operations are critical to achieving the desired material properties and must be carefully controlled to ensure consistent results. Temperature profiles, atmospheric conditions, and cooling rates all affect the final properties of the ceramic material. Advanced kiln designs and process control systems enable manufacturers to achieve the tight tolerances required for high-performance filter applications.
Testing and Validation
Comprehensive testing procedures are essential to ensure that ceramic filters meet all performance specifications and reliability requirements. Electrical testing includes measurement of frequency response, insertion loss, return loss, and power handling characteristics across the specified operating conditions. Environmental testing validates performance under temperature cycling, humidity exposure, vibration, and shock conditions.
Statistical process control techniques are employed to monitor production consistency and identify potential quality issues before they affect delivered products. Accelerated life testing provides confidence in long-term reliability, particularly for applications where field replacement is difficult or impossible. Traceability systems ensure that all components can be tracked from raw materials through final delivery.
Future Developments and Trends
Advanced Materials Research
Ongoing research in ceramic materials science continues to yield new compositions with improved performance characteristics and expanded capabilities. Low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technologies enable the integration of multiple functions within single ceramic packages, including filtering, coupling, and impedance matching elements. These integrated solutions reduce system complexity while improving overall performance and reliability.
Nanotechnology applications in ceramic filter development are opening new possibilities for enhanced performance and novel functionality. Nanostructured ceramic materials can exhibit unique electromagnetic properties that enable new filter designs and improved performance characteristics. The incorporation of nanoparticles and nanostructures into ceramic matrices offers potential for significant advances in filter technology.
Integration and Miniaturization
The continuing trend toward system miniaturization is driving development of increasingly compact ceramic filter solutions that maintain or improve performance compared to larger conventional designs. Three-dimensional ceramic structures enable complex filter implementations in minimal space, while advanced packaging techniques provide environmental protection and electrical connectivity in compact configurations.
System-on-package and system-in-package approaches are becoming more common, with ceramic filters integrated alongside other RF components to create highly functional modules. These integrated solutions simplify system design and assembly while potentially improving overall performance through optimized component interactions and reduced parasitic effects.
FAQ
What are the key advantages of ceramic filters compared to traditional metal cavity filters
Ceramic filters offer several significant advantages over traditional metal cavity filters, including much smaller size and weight for equivalent performance, better temperature stability, and the ability to integrate multiple functions in a single package. The high dielectric constant of ceramic materials enables compact designs that can achieve performance comparable to much larger metal cavity filters, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
How do environmental conditions affect ceramic filter performance
High-quality ceramic filters are designed to maintain stable performance across wide temperature ranges and various environmental conditions. The low temperature coefficient of frequency ensures minimal drift in filter characteristics with temperature changes. However, extreme conditions such as rapid thermal cycling or exposure to corrosive environments may require special packaging and sealing considerations to maintain long-term reliability.
What factors determine the power handling capability of ceramic filters
The power handling capability of ceramic filters is primarily limited by thermal effects rather than material breakdown. Factors that influence power handling include the thermal conductivity of the ceramic material, the effectiveness of heat dissipation paths, and the temperature rise that the filter can tolerate while maintaining acceptable performance. Proper thermal management design is essential for high-power applications.
How are ceramic filters customized for specific frequency requirements
Ceramic filters can be customized for specific frequency requirements through careful design of the resonator geometry, material properties, and coupling mechanisms. The dimensions and shape of the ceramic elements determine the resonant frequencies, while the coupling between elements affects the bandwidth and filter response shape. Advanced electromagnetic simulation tools enable precise optimization of these parameters to meet specific performance requirements.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Ceramic Filter Technology
- Performance Characteristics and Advantages
- Applications and Market Requirements
- Design Considerations and Selection Criteria
- Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Future Developments and Trends
-
FAQ
- What are the key advantages of ceramic filters compared to traditional metal cavity filters
- How do environmental conditions affect ceramic filter performance
- What factors determine the power handling capability of ceramic filters
- How are ceramic filters customized for specific frequency requirements